Thrombophilia is a disorder of the blood clotting system in which the risk of thrombosis increases

Information about your thrombophilia genes will allow you to find the necessary prevention and timely treatment!
IT COULD SAVE YOUR LIFE!
What is a blood clot?
A blood clot is a blood clot that consists of clumped red blood cells - platelets and fibrin protein. Normally, these elements are responsible for blood clotting and serve a useful function: stopping bleeding. When a vessel is damaged, a blood clot forms in that area.
A blood clot is dangerous because it prevents blood from flowing freely through the blood vessels. Over time, it can break off and travel to the heart, lungs, and brain, cutting off blood flow to vital organs. The result is heart attack, stroke, gangrene, paralysis, and death.
A blood clot doesn't just form.
You need several factors: lifestyle, diseases, disorders in the thrombophilia genes!

Abnormalities in thrombophilia genes increase the RISK:
- development of cardiovascular diseases
- heart attack
- thrombosis
- bleeding
- infertility
- Miscarriage
- abortive pregnancy
- complications of pregnancy
THIS ANALYSIS IS NECESSARY IF

01 PLANNING A PREGNANCY.
At the planning stage, this test will help you know the risks of miscarriage and pregnancy complications and prevent them. So if you are planning a baby, this test is for you!

02 THERE ARE PREGNANCY COMPLICATIONS.
If there are already complications of pregnancy, and in our practice we met such severe patients who had a history of more than 10 miscarriages and after learning the cause - disorders in the thrombophilia genes, with the prescription of appropriate treatment, carried and gave birth to healthy babies!!!
Infertility, IVF failures, premature placenta detachment, intrauterine fetal delay, stillbirth, premature birth, and a history of antenatal fetal death are also indications for testing.
03 YOU ARE TAKING CONTRACEPTIVES.
Taking estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives combined with disorders in the F2 and F5 thrombophilia genes can lead to very dangerous health risks for you: thrombosis, bleeding, cardiovascular disease.
Therefore, this test is recommended before prescribing hormonal contraceptives.
04 FAMILY HISTORY.
If you or your relatives have had thrombosis, cardiovascular disease, heart attacks, strokes, this test is necessary for YOU to know your risks and be able to minimize them!

05 THERE ARE RISK FACTORS.
- Recent injuries and surgeries
- Stress
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Improper nutrition
- Environmental factors
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Smoking
Risk factors increase the likelihood of developing thrombophilia.

06 THERE WERE TROMBOSES.
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Thrombosis of mesenteric vessels
- Thrombosis of cerebral vessels
- Renal vein thrombosis
- Stroke
- Infarction
- Bleeding
Analysis of thrombophilia genes will help to work out in which part of the hemostasis system there is a disorder.
WHAT TYPES OF ANALYSIS ARE THERE?
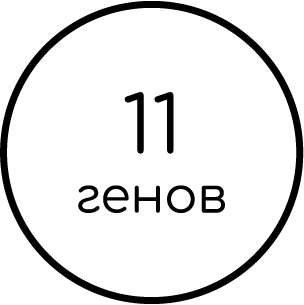
THROMBOPHILIA FULL PANEL
11 genes
![]()

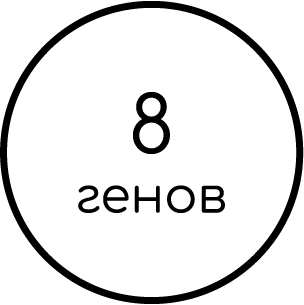
THROMBOPHILIA STANDARD PANEL
8 genes
![]()
![]()





FOLLAT REFERENCE
3 genes
![]()
![]()



THROMBOPHILIA 1 GENE
![]()
![]()
you can take one gene from the whole list
WHICH ANALYSIS TO CHOOSE?
FULL PANEL [ RECOMMENDED ]
It is recommended to take this panel because the analysis gives the most complete result.
Some genes work in opposition to each other and can compensate for each other accordingly. As a result, a geneticist at evaluates your risks, taking all the information into account.
You also get a personalized book with the opinion of a geneticist and a description of each gene and your individual risks with a transcript.
65 200 tenge



STANDARD PANEL
This thrombophilia panel without folate exchange genes. Recommended for increased susceptibility to thrombosis, arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction, CHD, ischemic stroke.
47,600 tenge



FOLLAT REFERENCE
It is recommended to establish the causes of elevated homocysteine levels, also for the prevention of some fetal congenital abnormalities.
17,800 tenge


RISK OF TAKING HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES
Recommended for planning and taking hormonal oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy during menopause.
11,800 tenge
⠀
THROMBOPHILIA GENES
It is also possible to take each gene separately, usually by doctor's order


F2 gene
PROTHROMBIN PROTEIN STRUCTURE AND FORMATION
Prothrombin or coagulation factor II is one of the main components of the blood coagulation system. As a result of its cleavage, thrombin, the basis of the thrombus, is formed. This reaction is the first stage in the formation of a blood clot. A mutation in the F2 gene leads to increased gene expression, i.e., excessive prothrombin production. This subsequently leads to increased thrombosis.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
RISKS: Fetal loss in the first trimester | Venous thrombosis | Increased risk of postoperative death | Ischemic stroke.


F5 gene
THROMBIN FORMATION FROM PROTHROMBIN
A mutation in the F5 gene makes the F5 factor resistant to the cleavage action of regulatory enzymes, resulting in hypercoagulability - increased blood clotting. Mutation in the F5 gene and taking hormonal contraceptives mutually increase their effect on the clotting system, which leads to a significant increase in the risk of thrombosis when they are combined.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
RISKS: Increased susceptibility to vascular thrombosis | Venous and arterial thromboembolism | Myocardial infarction and stroke | Early miscarriage | Fetal retardation | Late toxemia | Fetoplacental insufficiency


PAI-1 gene
PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR INHIBITOR GENE
The gene encodes a protein, endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor, belonging to SERPINE1 family. This protein inhibits, i.e. slows down tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase. These objects of the hemostasis system activate the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, which cleaves fibrin from clots. Thus, SER- PINE1 negatively affects fibrinolysis and prevents clot dissolution.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
RISKS: Thrombosis | Non-pregnancy | Preeclampsia (BP abnormalities in pregnancy)


FGB gene
THE STRUCTURE OF THE FIBRINOGEN PROTEIN.
Fibrinogen produces fibrin, the main component of the blood clot. Fibrin is the basis of the blood clot and subsequently forms a clot, completing the clotting process. A mutation of this gene increases the concentration of fibrinogen protein in the blood plasma, resulting in increased thrombosis.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
RISKS: Increased risk of ischemic stroke | Atherosclerotic changes in cerebral vessels | Myocardial infarction | Lacunar cerebral infarctions


ITG A2 gene
ENCODES ONE OF THE INTEGRINS, ALPHA-2 (ITGA2)
When the vessel wall is damaged, blood clotting is activated. Platelets stick together and close the damaged area at the very beginning of clotting. Aggregation occurs due to the presence of receptors on the surface of platelets, which are a complex of proteins-integrins. A mutation in this gene changes the properties of platelet collagen-binding receptors, which leads to an increase in the rate of platelet adhesion (sticking). The presence of the T allele is associated with a risk factor for thrombophilia.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
RISKS: Myocardial infarction | Coronary stroke | Thromboembolism , especially at a younger age | Thrombosis after coronary angioplasty and stenting


ITG B3 gene
ENCODES PROTEIN INTEGRIN BETA-3, A MEMBRANE GLYCOPROTEIN
This receptor ensures the interaction of platelets with blood plasma fibrinogen, resulting in platelet adhesion and thrombus formation. platelets of carriers of the C allele have an increased tendency to aggregation and, as a result, increased thrombus formation. The study of the gene is important in determining the risk of hip fractures, especially in postmenopausal women and against the background of the use of hormone replacement therapy. It is also informative in evaluating the effectiveness of aspirin therapy (its antiaggregant properties).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
RISKS: Cardiovascular disease (myocardial infarction) | Thromboembolism | Early termination of pregnancy due to placental thrombosis | Disorders of antiaggregant effectiveness


F7 gene
FORMATION OF CLOTTING FACTOR VII
The main role of F7 is the activation of prothrombin formation. With mutations in the F7 gene, there is a decrease in F7 activity, which results in a corresponding decrease in prothrombin formation. Ultimately, the chain reduces thrombin formation. Expression of this gene contributes to a decrease in thrombosis and is a protective factor in the development of thrombosis and myocardial infarction.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
RISKS: Reduced thrombosis | Risk of bleeding


F13 gene
FACTOR XIII IS A PROTEIN INVOLVED IN BLOOD CLOTTING
Activated protein F13a promotes "cross-linking" of fibrin monomers, which leads to the formation of fibrin-polymer. Fibrin-polymer is the basis of the blood clot, which stabilizes the clot, completing the process of blood clotting. Due to the mutation, the biochemical properties of the F13 protein are transformed, resulting in thinner fibrin clots and loss of their stability to proteases. Thus, changes in this gene in most cases are aimed at providing a protective effect. A decrease in the activity of these factors contributes to a decrease in thrombosis.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
RISKS: Increased risk of delayed bleeding
HEMOSTASIS SYSTEM
The diagram shows in which parts of the hemostasis system specific genes are involved
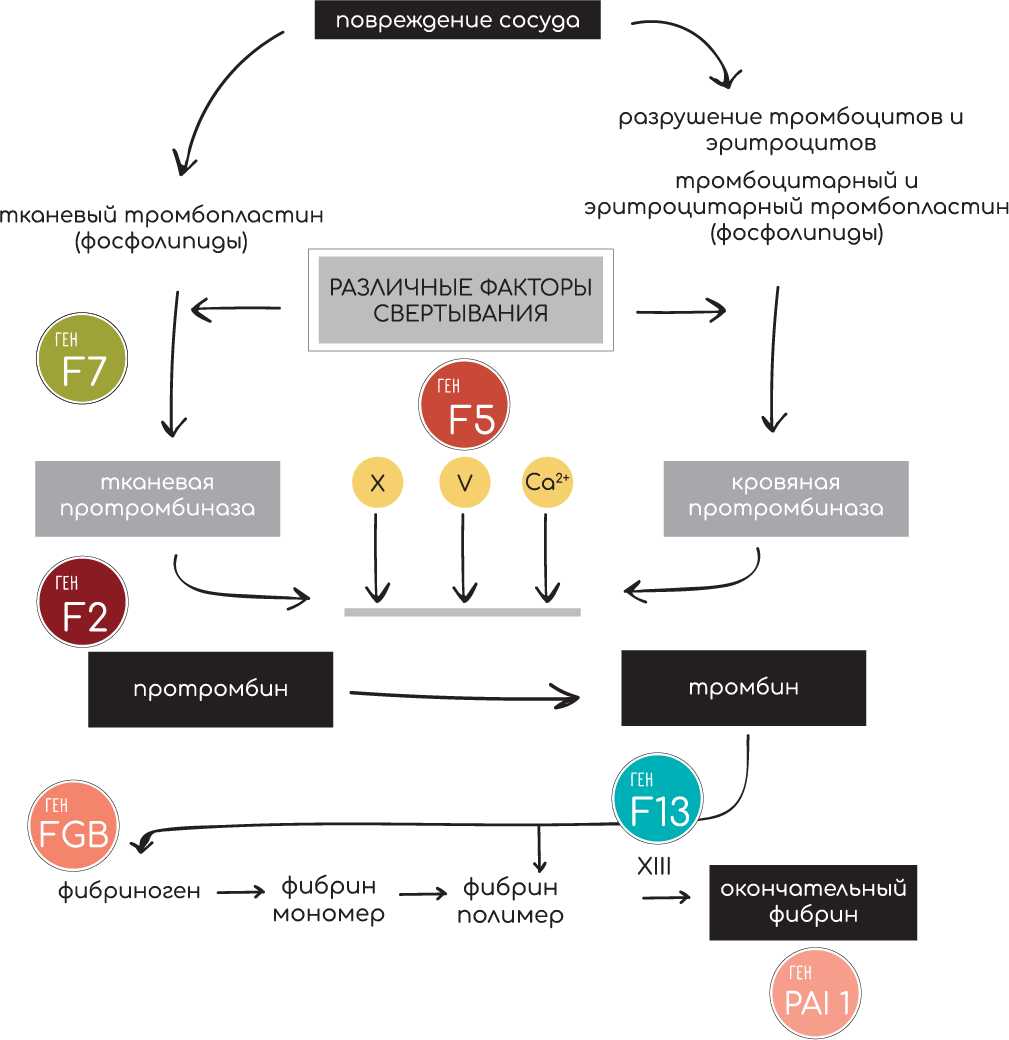

HEMOSTASIS INCLUDES


PRIMARY HEMOSTASIS
local narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels - to reduce blood flow to the injured area formation of a platelet "plug"


SECONDARY OR PLASMA HEMOSTASIS
interaction between numerous factors and clotting inhibitors.


FIBRINOLIS
the process by which a clot dissolves after the integrity of the damaged vessel wall has been restored.
VIDEO CONSULTATION: Thrombophilia genes and pregnancy
Says: Rakisheva Zere Bayanovna, Candidate of Medical Sciences, physician-geneticist of TreeGene laboratory.
- What is thrombophilia
- risk groups
- Who is recommended to be tested for thrombophilia genes
- clotting system genes
- results of the analysis and recommendations for the doctor
WHAT'S THE RESULT?


A DOCTOR'S REPORT FROM A GENETICIST
We provide a report from a geneticist with recommendations for the attending physician, that is, you get a transcript of the result.


CONSULTATION WITH A GENETICIST
We also have a geneticist, to whom you can make an appointment, get a consultation and get answers to your questions (the cost is 7,000 tenge).
sign up

RESULT RELIABILITY
We work according to the international standard ISO 15 189, we use only quality reagents and equipment, so you can be sure of the reliability of the results! Every year our laboratory undergoes an external quality evaluation by the RfB (Germany).
certificatesHOW TO TAKE THE TEST?
01
SIGN UP NOW
blood from a vein or buccal epithelium (saliva) in a way that is convenient for you:
02
PAY
In cash, online, by card or via bank
03
SCORE
Pick up in person/mail/satp in 7 business days