THE TEST IS TEMPORARILY SUSPENDED!
Analysis for predisposition/risk of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS).
In 5-15% of women, PCOS is the cause of infertility, miscarriage, complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
WHAT IS POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME?

Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a complex disorder accompanied by disorders of the ovaries, disrupted functions of the pancreas, hypothalamic-pituitary system, and adrenal cortex. As a result of such a complex hormonal failure, a woman's menstrual cycle is disrupted, there is no ovulation, which leads to infertility, and she becomes overweight.
THE REASON OF POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME:
01
Genetic predisposition has a great influence in the occurrence of polycystic ovaries : the presence of mutations in the genes that control glucose metabolism in the body and in the genes responsible for steroid synthesis in women.
02
When there is a disorder in the genes that control glucose metabolism, the cells become resistant (unresponsive) to insulin. All cells in the body except the ovaries.
03 Increased insulin in the blood stimulates the production of male hormones, which decreases women's fertility. Increased steroids in a woman's body also lead to polycystic ovaries and infertility. And when there is a disorder in the genes responsible for steroid production, the clinical picture of this disease in women is exacerbated.
WHO IS ELIGIBLE FOR THE TEST

01CYCLE DISRUPTION.

02BIRTHLESS.

03OVERWEIGHT.

04OVARIAN CYSTS.

05ALOPECIA.

06PROBLEMATIC SKIN.
WHAT CAN WHAT DOES PSEUDO-PSYCHOSIS LEAD TO?
- Infertility (due to lack of ovulation), and primary, which is characterized by the absence of pregnancy in the history of women (as opposed to secondary infertility, in which reproductive failure develops after pregnancies that end in childbirth, miscarriages or abortions)
- Failure to conceive
- Uterine myoma, hyperplasia, and endometrial cancer
- Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system: coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, hypertension
- Obesity, found in 40% of PCOS patients, is a manifestation of metabolic disorders and is characterized by either an even distribution of fat deposits throughout the body (universal type of obesity), or predominant deposition of fat in the abdomen and waist (male type of obesity)
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Cancer burden
- Severe liver dysfunction
Recently, PCOS has been increasingly associated with the metabolic syndrome, when there is excess body weight, insulin resistance with compensatory hyperinsulinemia. The incidence of metabolic syndrome in women with PCOS is 1.6-43%.
DIAGNOSTICS POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME:
The difficulty in diagnosing this pathological condition is that the functional activity of the pituitary gland, ovaries, adrenal glands, and hypothalamus are interrelated - the lesion of any of these organs affects the condition and function of other parts of the reproductive system. Often patients are prescribed many expensive procedures and various tests to clarify the diagnosis.
Meanwhile genetic research in this disease will make it much easier to make an accurate and comprehensive diagnosis and prescribe early treatment, without waiting for severe complications and consequences. The most important thing in this disease - it is timely diagnosis and treatment. Today, PCOS can be controlled and treated in 90% of cases.
WHAT GENES ARE BEING TESTED
genes that control metabolic processes of glucose metabolism - conditions of hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance

INSULIN GEN.
Encodes a proenzyme that is synthesized by beta cells of pancreatic Langerhans islets and thymus cells. Carriage of unfavorable alleles can be a risk factor for abdominal obesity and predispose to the development of type 2 diabetes. At the same time, carriage of unfavorable alleles predisposes to the development of permanent and transient NCD, DM in young children, and MODY type DM.

PEROXISOME GAMMA-2 RECEPTOR.
A gene that regulates fat accumulation, adipocyte differentiation (fat cells), and myoblasts. Adverse alleles are a risk factor for obesity, insulin resistance, and the development of type 2 diabetes.
genes that are responsible for the synthesis of steroid hormones and individual tissue sensitivity to androgens.

(androgen receptor gene) - the gene is associated with tissue sensitivity to androgens. The study of the polymorphism of this gene is diagnostically important in determining the risk of a classic (accompanied by elevated testosterone) form of PCOS.

gene responsible for the initial stage of steroid hormone synthesis. Information about CYP11A polymorphism helps to develop a proper management plan for patients with signs of hyperandrogenism, metabolic syndrome, and alopecia.

encodes the luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor. The receptor allows the body to respond to stimulation by these hormones. In women, luteinizing hormone is responsible for the release of eggs from the ovaries (ovulation); chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone that starts to be produced by the chorionic tissue after embryo implantation, is one of the most important indicators of pregnancy and its successful development.
THAT AS A RESULT OF
Why take a genetic test
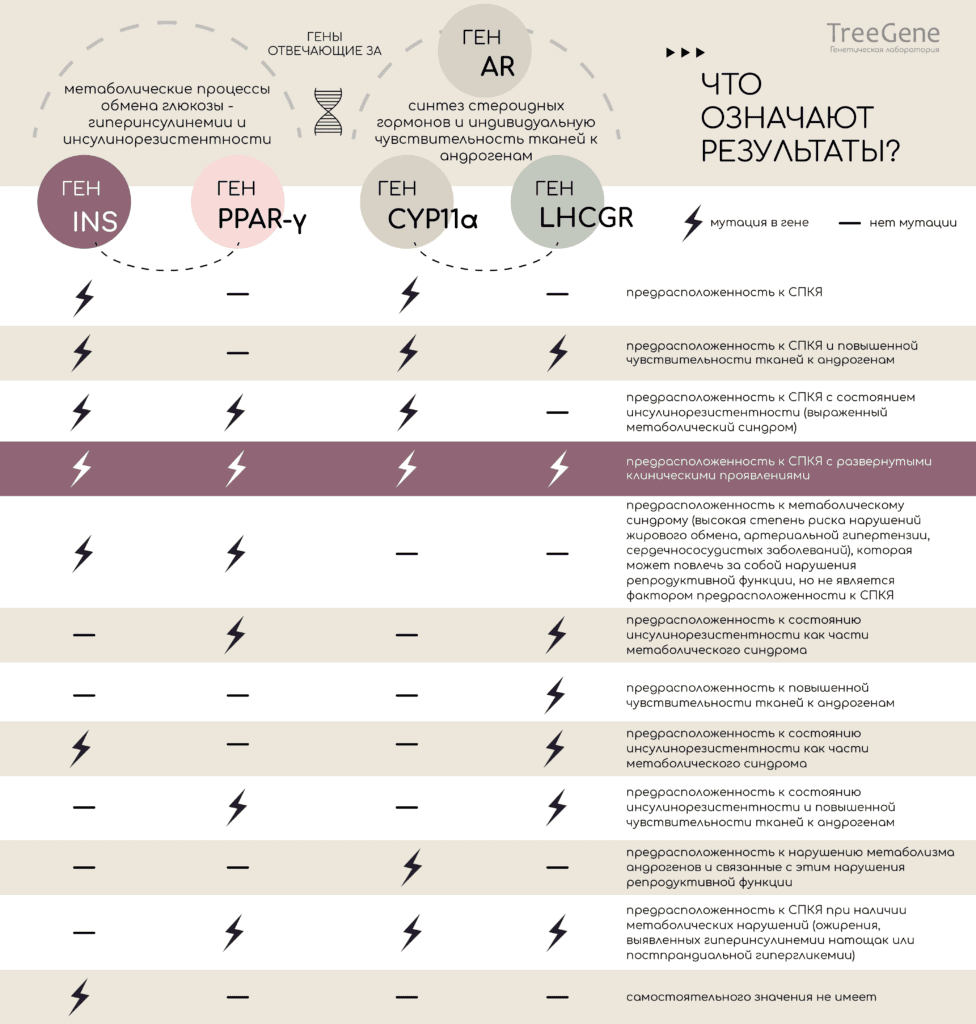
- The analysis shows the presence of mutations in one of the five genes.
- The presence of changes in each of the genes indicates the likelihood of one or another problem: predisposition to metabolic syndrome; predisposition to impaired androgen metabolism and related reproductive disorders; predisposition to PCOS in the presence of metabolic disorders, etc.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome can help women with infertility problems, improve skin and hair, and most importantly, reduce the risk of complications such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart and liver disease.
HOW TO TAKE THE TEST?
01
SIGN UP NOW
blood from a vein or buccal epithelium (saliva) in a way that is convenient for you:
02
PAY
In cash, online, by card or via bank
03
SCORE
Pick up in person/mail/satp in 18 business days
TIMES
30
business days
The analysis will allow the physician to identify the cause-and-effect relationship of the various clinical manifestations of PCOS and help in the choice of treatment methods.
order