| Chlamydia trachomatis (Ch. trachomatis) by real time PCR | Price 1 800 tenge |
Urogenital chlamydia is an infectious disease caused by certain serotypes of Chlamydia trachomatis, which is sexually transmitted and mainly affects the urogenital system. According to WHO, up to 90 million people worldwide become ill with urogenital chlamydia each year. It is sexually transmitted.
The causative agent Chlamydia trachomatis has the following important characteristics:
 Intracellular parasitization, which unites chlamydiae with viruses, and chlamydiae are unable to synthesize ATP and are totally dependent on the energy resources of the cell - i.e. in the process of parasitization they destroy it completely
Intracellular parasitization, which unites chlamydiae with viruses, and chlamydiae are unable to synthesize ATP and are totally dependent on the energy resources of the cell - i.e. in the process of parasitization they destroy it completely- The presence of a cell membrane unites chlamydiae with bacteria - this allows the use of antibiotics to treat chlamydia
- Tropism to the cylindrical epithelium of certain organs (urogenital organs, conjunctiva)
- Having a unique life cycle
Symptoms:
After an incubation (latent) period, the duration of which depends on the amount of chlamydia in the body and the local immune defense (on average 7 to 20 days), the first clinical symptoms (signs) of the disease appear. Because chlamydia infects only certain cells - the cylindrical epithelium - chlamydia is characterized by a favorite localization - that is, colonization and reproduction of chlamydia in certain human organs. These are the mucosa:
- urethra
- cervical canal in women
- posterior pharyngeal wall
- rectum
- conjunctiva of the eye
Very often chlamydia is asymptomatic, less often with minimal manifestations. When it affects the urinary and genital organs, it is a feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen and impaired urination. A total of 46% of men and 67% of women experience chlamydia without symptoms. Even without treatment of chlamydia, the symptoms sometimes disappear after a couple of weeks. Chlamydia becomes chronic with the risk of complications and transfer of infection to other organs.
The TreeGene laboratory can test for Chlamydia trachomatis by PCR:
- Detection of Candida albicans by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This method is considered the most sensitive method for diagnosing infections, and is based on the detection of the infectious agent's DNA in the material.
How to properly prepare for the study?
A scrape is required for the study.
- It is recommended that women take a urogenital swab or urine sample before their period or two days after their period ends.
- Women and men should not urinate for 3 hours before taking a smear.

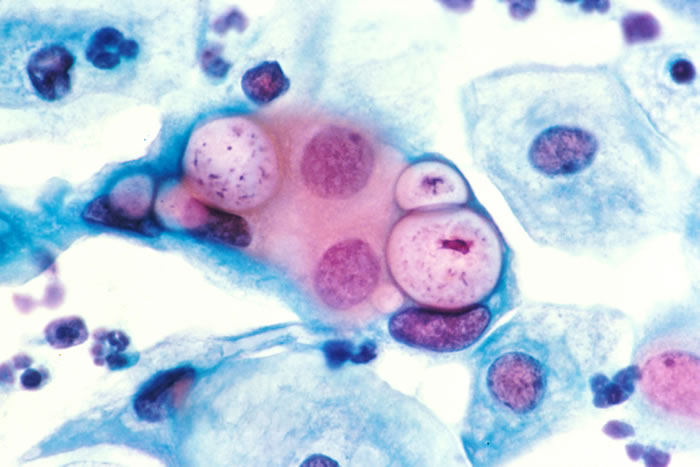 Intracellular parasitization, which unites chlamydiae with viruses, and chlamydiae are unable to synthesize ATP and are totally dependent on the energy resources of the cell - i.e. in the process of parasitization they destroy it completely
Intracellular parasitization, which unites chlamydiae with viruses, and chlamydiae are unable to synthesize ATP and are totally dependent on the energy resources of the cell - i.e. in the process of parasitization they destroy it completely