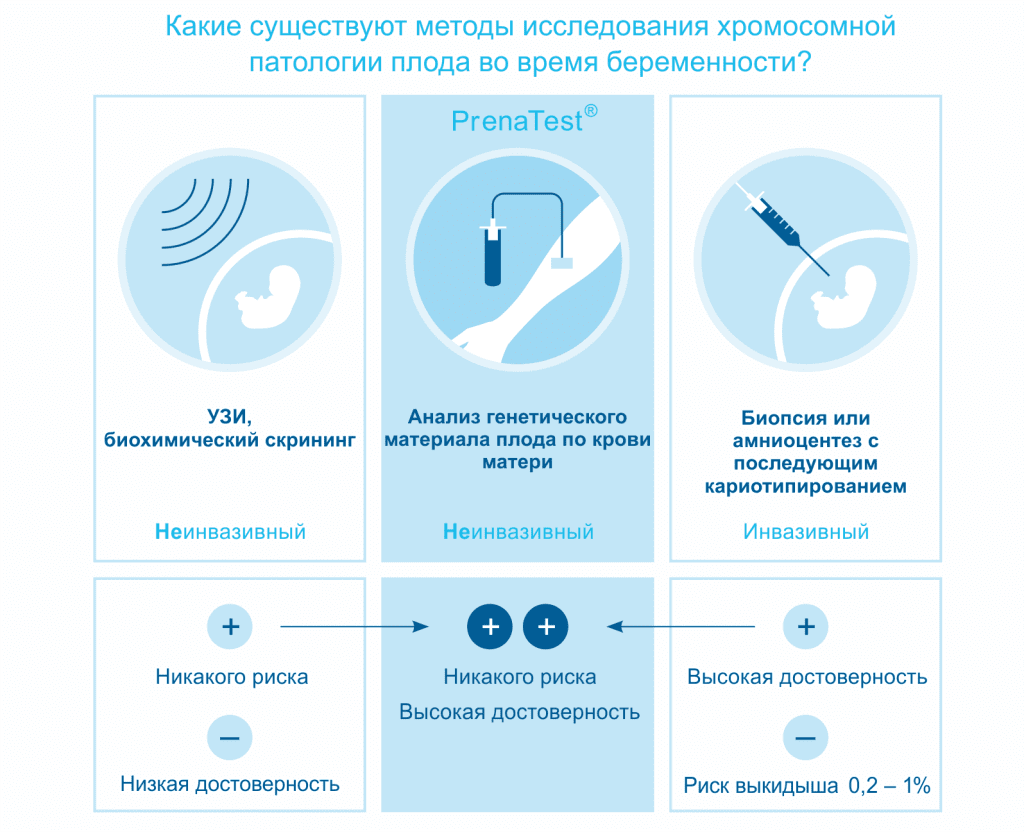
Prenatal diagnosis of trisomy in Kazakhstan is performed for all patients in both private and public institutions. Based on biochemical screening and ultrasound data, the risk of a fetus being born with a chromosomal abnormality is determined. In cases of high risk, invasive prenatal diagnosis (chorionic villus sampling, placentocentesis, amniocentesis, cordocentesis) followed by karyotyping is recommended.
90% of all chromosomal abnormalities in newborns are trisomic 13, 18, and 21 pairs of chromosomes. Down syndrome accounts for 75% of them (L.V. Akulenko, T.V. Zolotukhina).
Despite significant technical advances in prenatal diagnosis, all invasive procedures remain associated with some risk of pregnancy termination, especially for older women. Therefore, the performance of invasive procedures should be seriously motivated.
A new "non-invasive" and safe approach in prenatal diagnosis involves the study of cells, extracellular DNA fragments and fetal RNA circulating in the peripheral blood of the mother.Free floating fetal DNA in maternal blood comes from trophoblast cells, so the reliability level of the study is comparable to a sample directly from the chorion.
PrenaTest® is a test that combines the benefits of traditional methods and is also safe for the unborn child.